Difference between revisions of "project02:Frontpage"
(→parameters) |
(→inspiration & references) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
[[File:matrix.jpg| 850px]] | [[File:matrix.jpg| 850px]] | ||
| + | <i>source: Movie - The matrix</i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:collage_2.jpg| 850px]] | ||
<i>source: Movie - The matrix</i> | <i>source: Movie - The matrix</i> | ||
Revision as of 23:23, 1 November 2016
We are having a problem!
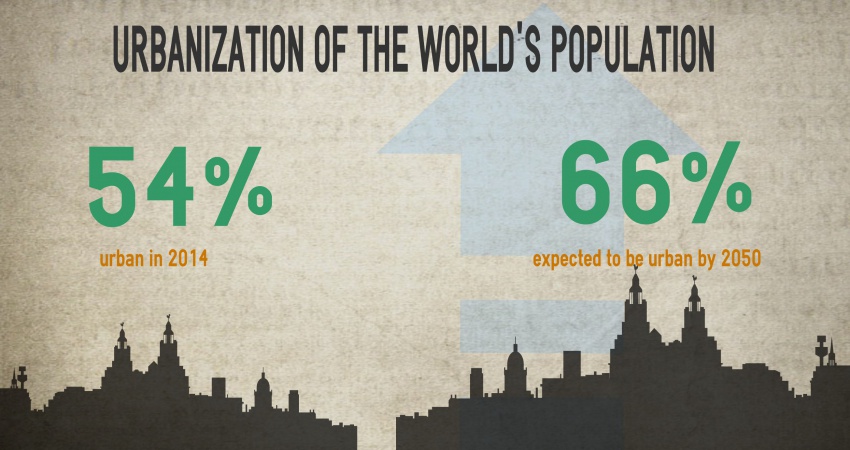 source: United Nations, Department of Economics and Social Affairs, Population Division
source: United Nations, Department of Economics and Social Affairs, Population Division
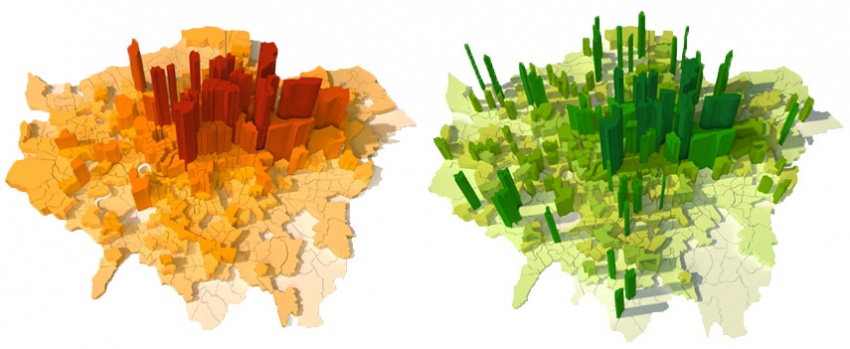 Possible outcomes of population growth in london by 2050
Possible outcomes of population growth in london by 2050
What if?
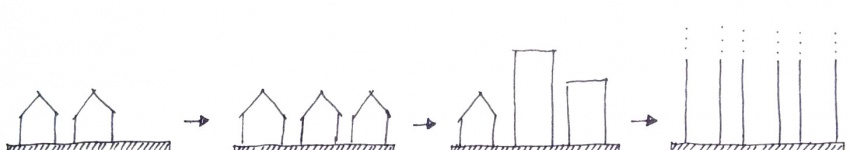
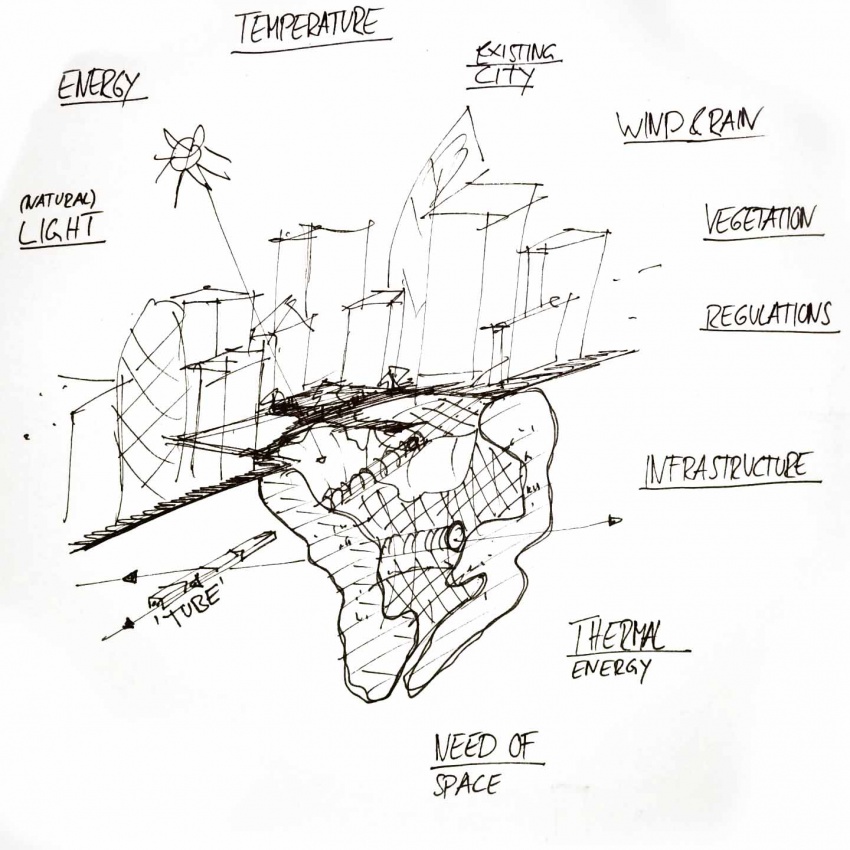
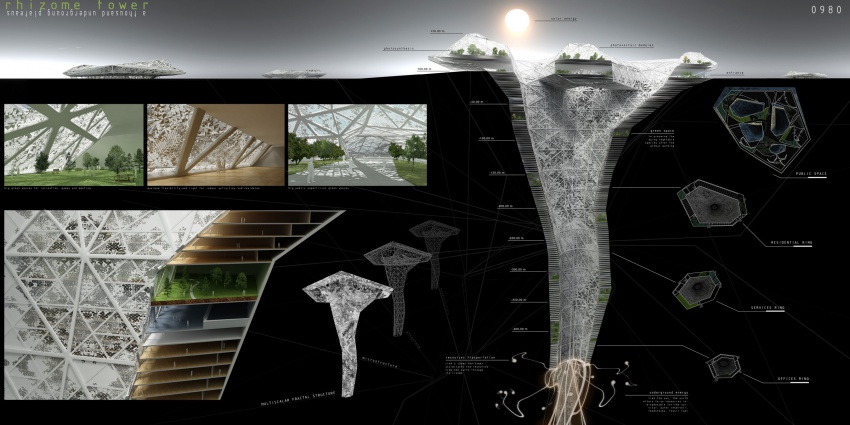
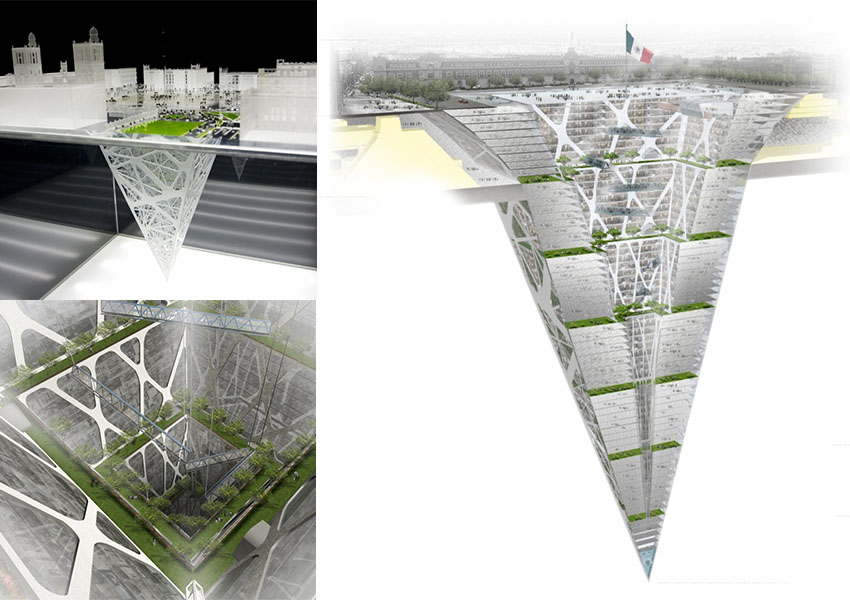
Instead of building unlimited high-rise buildings, what if one would start building into the ground? What if one would use the public spaces of cities to transform them into “invisible” buildings, which leave already existing free space to the public? These underground parts of the city could offer a new urban level; they could solve the problem of necessary accommodation. One could build these buildings without visually disturbing construction sites, one could build them according to natural principles and one could build them completely energy neutral to achieve a fully ecological architecture. An underground earthscraper would not need to resist high wind loads and it would not need high amounts of insulation. It would make use of e.g. geothermal energy or ground water. One of the biggest challenges though is the supply with essential daylight, which is needed to grow plants as well as for personal well-being. To achieve an equal or even better atmosphere, it will be necessary to make use of computational methods in planning and robotic fabrication during the construction process. Computational methods and simulations can help to provide a maximum of sunlight and to optimize the building's shape and structure.
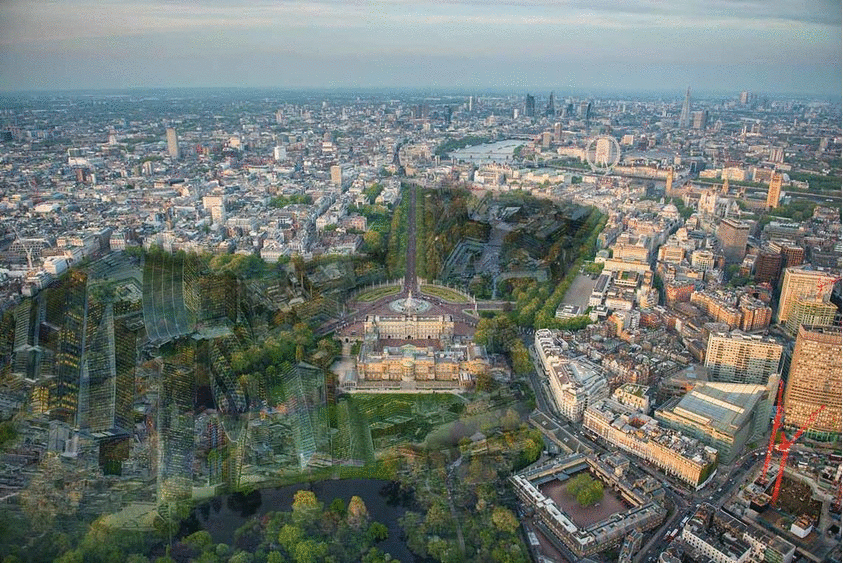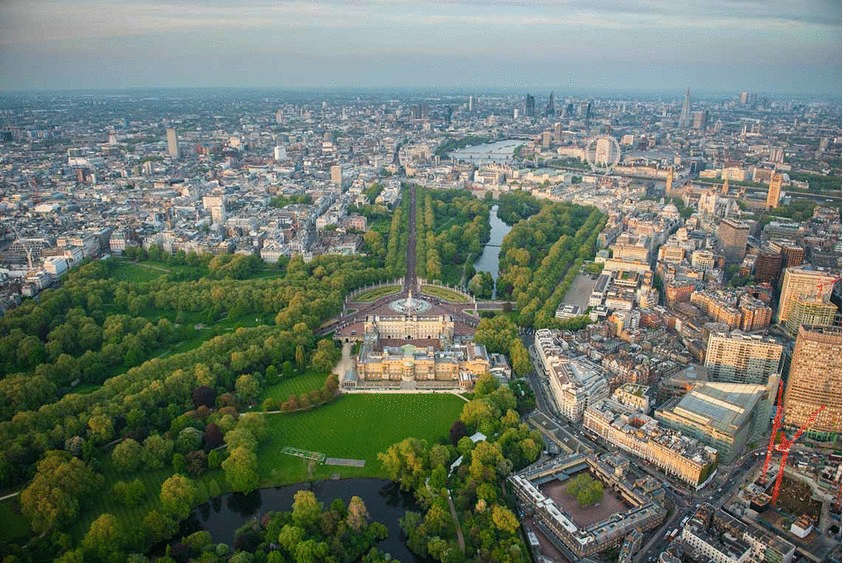
possible locations
In my opinion, all publich places which have a certain size can potentially be considered to build underground. But especially parks could be target locations. As long as the final deisgn keeps all benefits of a public park and combines them with space to live or work, I think one shall speak of an architectural improvement.