Difference between revisions of "project02:Frontpage"
From rbse
(→possible locations) |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ __NOTITLE__ | __NOTOC__ __NOTITLE__ | ||
| + | [[File:ecotourism_title_top.jpg| 850px]] | ||
| + | <div style="height:30px; width: 870px; margin:0px; padding: 0px; padding-top: 20px; border: 0px;"> | ||
| − | <div style=" | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 2px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:Frontpage|'''Concept''']]</div> |
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:P1|'''Prototypes''']]</div> | |
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | |
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:P2|'''P2 ''']]</div> |
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:P3|'''P3 ''']]</div> |
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:P4|'''P4 ''']]</div> |
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:diverse|'''Media Studies ''']]</div> |
| − | <div style="float:left; width: | + | <div style="float:left; width: 109px; height 30px; font-color: #ffffff; border: 1px solid #000000; background-color: #ffffff; margin-right:10px;" align="center">[[project02:comments|'''Comments''']]</div> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
| + | == Situation == | ||
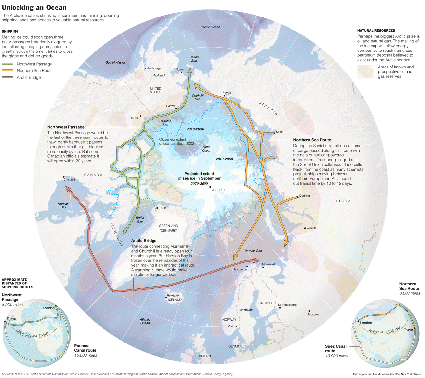
| + | <div style="float:left;">Climate in the arctic is changing drastically. It is expected that two main effects are going to happen until 2030: First, the arctic ice will have melted to an extend, which is going to make it possible to ship the so called Nort-West passage. One can already see a groing trend of ships using this way shorter route between Europe and the West coast of the US and Canada. Second, the arctic is turning green. That results in a shift of the treeline, in more vegetation in general and in an increase of overall temperature by huge numbers. The arctic is heating up almost twice as fast as the rest of the planet. The permafrost layer, which incorporates roughly 50% of the worlds carbon dioxide is in danger. But there will also be effects on nature. | ||
| − | + | <html> | |
| − | < | + | <iframe width="850" height="478" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/Yi8SFOJffFA" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> |
| + | </html> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:20051010 ARCTIC GRAPHIC.gif| 425px]] |
| − | < | + | [[File:ecotourism.gif| 420px]] |
| + | |||
| + | == Canada’s Arctic an Untapped Gold Mine … of Tourism! == | ||
| + | <div style="float:left;">With a declining mining industry, Canada is looking for new models of economy. Arctic eco tourism has already started growing over the last decade and is expected to grow even more rapid in future. This brings the chance of economic growth and employment. But it is also a dangerous situation for nature. Since the canadian north is to more than 98% untouched, uncontrolled growth of traditional building complexes must not destroy nature as is already did in the south. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | == Concept == | |
| + | <div style="float:left;">The concept suggests to combine two aspects of canadian past with one of the future. The declared goal is not to destroy anymore nature by infrastructure of insensible buildings for tourism. The site of the Diavik Diamon Mine has been chosen for two things: First, to renaturalize the area by money made from tourism. Second, to build an invisible starting point for eco tourism in this area. THe huge holes, which have been the result of a process called open-pit-mining, are a perfect spot to implement a building on a site from which nature was already banished. Another main point is to use the old airfield as infrastructure for tourism. No additional streets need to be build. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:161204_GoogleMaps_Satelite_Diavik_Zoom1.gif| 850px]] | ||
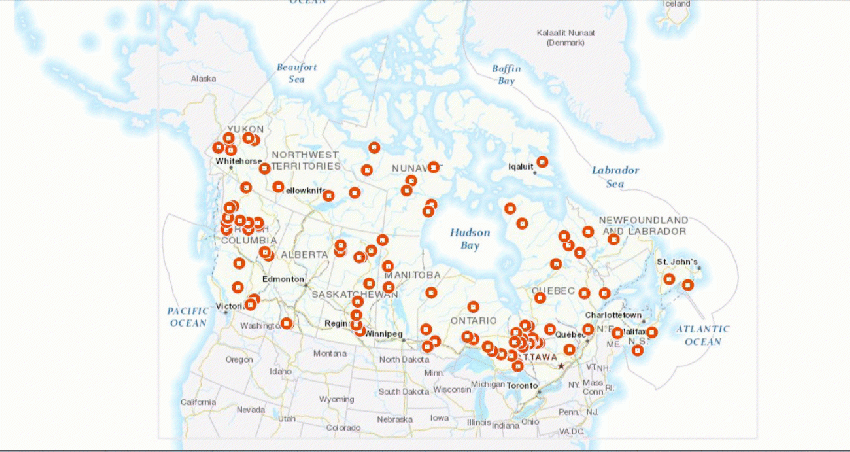
| − | + | Similar to this site, there are much more in Canada. It might be a strategy to connect them to a tourism network which offers different experieces in diferent sites. The following maps shows the 100 biggest open-pit mines in the country. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[File:Output_jypMCB.gif| 850px]] | |
| − | + | == site == | |
| − | + | <div style="float:left;">The chosen site is the area of the Diavik Diamon Mine in the Nortwestern Terretoies of Canada. This mine is estimated to stop production in 2025 to move some other place and start again. This site is strategically well positioned to establish eco tourism, because of two main reasons: First: It is almost in the middle between the arctic coast and the southern population boundaries. Therefore it is posssible to access the site from both direction time efficietly. Second, this mid-canadian area is not estimated to have much more mineral ressource, which will result in no more industrial area to disturb nature. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | <html> |
| − | + | <iframe src="https://www.google.com/maps/d/embed?mid=1W7-A9xYjyAnRAy0ONqhduWtJc74" width="850" height="500"></iframe> | |
| + | </html> | ||
| − | + | [[File:161205_Before&After.gif| 850px]] | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | [[File: | + | |
| − | < | + | |
| − | == | + | == Design == |
| − | + | ... about to come | |
| − | ==robotic | + | == robotic production == |
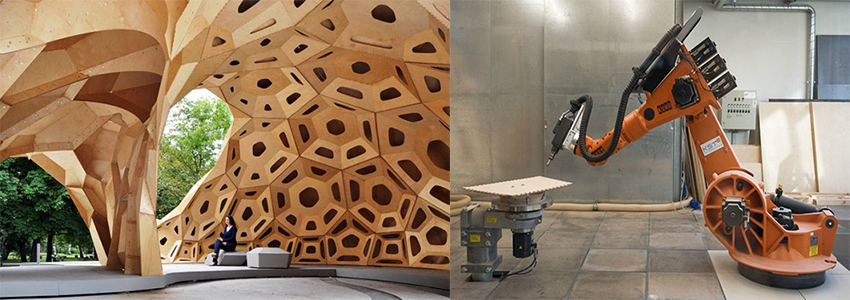
| − | + | <div style="float:left;">I see ahuge potential to use robotic (pre)fabrication with the material wood. Since there is no infrastructure available on site, it is necessary to produce all parts of the building in components which only need to ba assembled on site. | |
| + | <br> | ||
| − | + | [[File:wood_pic.jpg |850px]] | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:clt_pic.jpg |850px]] |
| − | < | + | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | + | <!-- |
| − | <i>source: | + | [[File:urban_development.jpg| 850px]] |
| + | <i>source: United Nations, Department of Economics and Social Affairs, Population Division</i> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | --> | |
Latest revision as of 21:58, 26 March 2017
Situation
Climate in the arctic is changing drastically. It is expected that two main effects are going to happen until 2030: First, the arctic ice will have melted to an extend, which is going to make it possible to ship the so called Nort-West passage. One can already see a groing trend of ships using this way shorter route between Europe and the West coast of the US and Canada. Second, the arctic is turning green. That results in a shift of the treeline, in more vegetation in general and in an increase of overall temperature by huge numbers. The arctic is heating up almost twice as fast as the rest of the planet. The permafrost layer, which incorporates roughly 50% of the worlds carbon dioxide is in danger. But there will also be effects on nature.
Canada’s Arctic an Untapped Gold Mine … of Tourism!
With a declining mining industry, Canada is looking for new models of economy. Arctic eco tourism has already started growing over the last decade and is expected to grow even more rapid in future. This brings the chance of economic growth and employment. But it is also a dangerous situation for nature. Since the canadian north is to more than 98% untouched, uncontrolled growth of traditional building complexes must not destroy nature as is already did in the south.
Concept
The concept suggests to combine two aspects of canadian past with one of the future. The declared goal is not to destroy anymore nature by infrastructure of insensible buildings for tourism. The site of the Diavik Diamon Mine has been chosen for two things: First, to renaturalize the area by money made from tourism. Second, to build an invisible starting point for eco tourism in this area. THe huge holes, which have been the result of a process called open-pit-mining, are a perfect spot to implement a building on a site from which nature was already banished. Another main point is to use the old airfield as infrastructure for tourism. No additional streets need to be build.
Similar to this site, there are much more in Canada. It might be a strategy to connect them to a tourism network which offers different experieces in diferent sites. The following maps shows the 100 biggest open-pit mines in the country.
site
The chosen site is the area of the Diavik Diamon Mine in the Nortwestern Terretoies of Canada. This mine is estimated to stop production in 2025 to move some other place and start again. This site is strategically well positioned to establish eco tourism, because of two main reasons: First: It is almost in the middle between the arctic coast and the southern population boundaries. Therefore it is posssible to access the site from both direction time efficietly. Second, this mid-canadian area is not estimated to have much more mineral ressource, which will result in no more industrial area to disturb nature.
Design
... about to come